Windows PowerShell depends on .NET framework 2.0. SQL Server Management Objects, known as SMO, is an object model for SQL Server and its configuration settings. SMO-based applications use .NET Framework languages to program against this in-memory object model, rather than sending Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands to SQL Server to do so.
In this article series, I am going to illustrate the power of Windows PowerShell in conjunction with SQL Server 2005. Part I of this series is going to illustrate how to install and use a simple PowerShell command and a simple SMO command.
Assumption
a. The machine you use already has .NET 2.0 installed b. The machine you use already has SQL Server 2005 client installed with the latest service pack Download and Install Microsoft PowerShell.
Download Microsoft PowerShell “WindowsXP-KB926139-x86-ENU.exe” from http://download.microsoft.com/
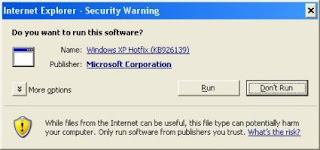
b. Install PowerShell Step 1: Double click on the “WindowsXP-KB926139-x86-ENU.exe’ executable. [Refer Fig 1.0]

Fig 1.0
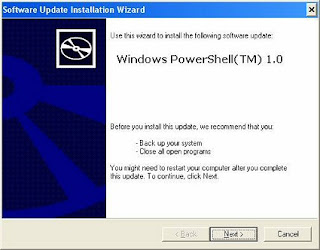
Launch PowerShell
There are few ways to launch PowerShell. One method is to go to the command prompt and type the following command. [Refer Fig 1.6]
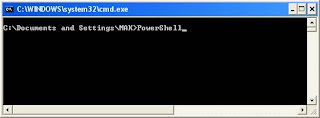
After a short pause, the PowerShell prompt appears. [Refer Fig 1.7]
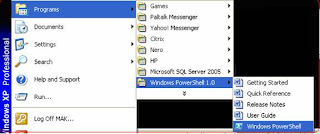
Alternatively, you can start PowerShell by selecting Programs-Windows PowerShell 1.0-Windows PowerShell. [Refer Fig 1.8]


No comments:
Post a Comment